카테고리 없음
[Project2][Springboot] 초기설정
321
2021. 5. 28. 13:36
sts를 사용해서
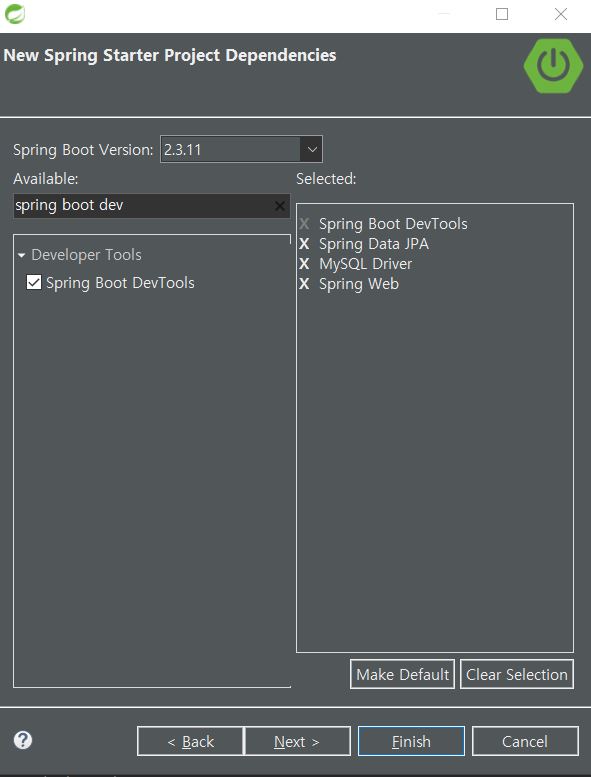
프로젝트 만들기
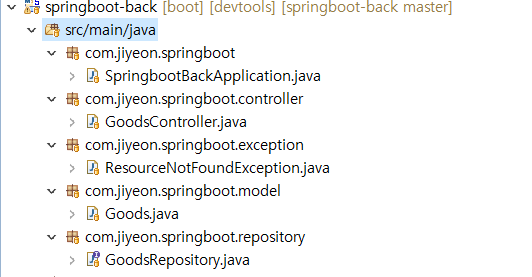
다음에 위와 같이 패키지 & 클래스 만들어준다.
- SpringbootBackApplication.java
package com.jiyeon.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootBackApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootBackApplication.class, args);
}
}
가장 상위 클래스이다. 스프링부트를 실행할 때 사용되는 클래스. @SpringbootApplication어노테이션을 붙여주면서 적용한다.
- GoodsController.java
package com.jiyeon.springboot.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.jiyeon.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import com.jiyeon.springboot.model.Goods;
import com.jiyeon.springboot.repository.GoodsRepository;
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/")
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsRepository goodsrepository;
//list
@GetMapping("/goods")
public List<Goods> getAllGoods(){
return goodsrepository.findAll();
}
//create
@PostMapping("/goods")
public Goods createGoods(@RequestBody Goods goods) {
return goodsrepository.save(goods);
}
//get by id rest api
@GetMapping("/goods/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Goods> getGoodsById(@PathVariable Long id) {
Goods goods = goodsrepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("goods not exist id : "+id));
return ResponseEntity.ok(goods);
}
//update
@PutMapping("/update-goods/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Goods> updateGoods(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Goods goodsDetails){
Goods goods = goodsrepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("goods not exist id : "+id));
goods.setName(goodsDetails.getName());
goods.setCompany(goodsDetails.getCompany());
goods.setPrice(goodsDetails.getPrice());
Goods updatedGoods = goodsrepository.save(goods);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedGoods);
}
//delete
@DeleteMapping("/delete-goods/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Boolean>> deleteGoods(@PathVariable Long id){
Goods goods = goodsrepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("goods not exist id : "+id));
goodsrepository.delete(goods);
Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}
- 스프링의 컨트롤러같은 클래스이다. 이런 거 몇 개 더 만들면 카테고리 생성도 가능하겠음
- 스프링 만들 때랑 나머지는 다 비슷한데 @CrossOrigin 어노테이션은 리액트랑 연결할 때 사용된 것.
- ResourceNotFoundException.java
package com.jiyeon.springboot.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
- 예외처리 전문 클래스
- Goods.java
package com.jiyeon.springboot.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="goods")
public class Goods {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private String company;
@Column
private double price;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, String company, double price) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.company = company;
this.price = price;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
- 엔티티 클래스 @Entity
- Setter Getter 생성자 만든다. (vo처럼)
- 어떤 테이블에서 무슨 역할하는지까지 정해주고 나중에 불러올 때도 자동으로 인식한다.
- GoodsReposiroty
package com.jiyeon.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.jiyeon.springboot.model.Goods;
@Repository
public interface GoodsRepository extends JpaRepository<Goods, Long>{
}
- JPA를 사용할 수 있게해 줌 - sql문없이 자동인식해서 실행하게 해줌
- application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/goods_management_system?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=mysql
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
- db연결 시 설정값. root-context에서 했던 역할들
- mysql 써서 문법에 맞게 포트번호와 username password 등 맞춰줌